
MENUMENU
TALK TO AN EXPERT
Special Hours: 7AM – 6PM PST
TALK TO AN EXPERT
Special Hours: 7AM – 6PM PST
Electric fuses are an integral part of almost all electrical circuits in our homes, vehicles, appliances, and components that we use every day. But what are fuses exactly? How do they function, and what is their purpose? This comprehensive guide breaks down the science of fuses and explains why they’re essential for electrical safety.
An electric fuse is a device that protects a circuit by interrupting current flow when excessive current causes its internal element to melt or separate. Think of it as an intentional “weak link” in your circuit. This means that when something goes wrong, the fuse sacrifices itself to protect everything else.
Fuses are installed in electrical circuits as small as a microchip (.01 amps) and as large as power/ motor grid-sized (10,000 amps)
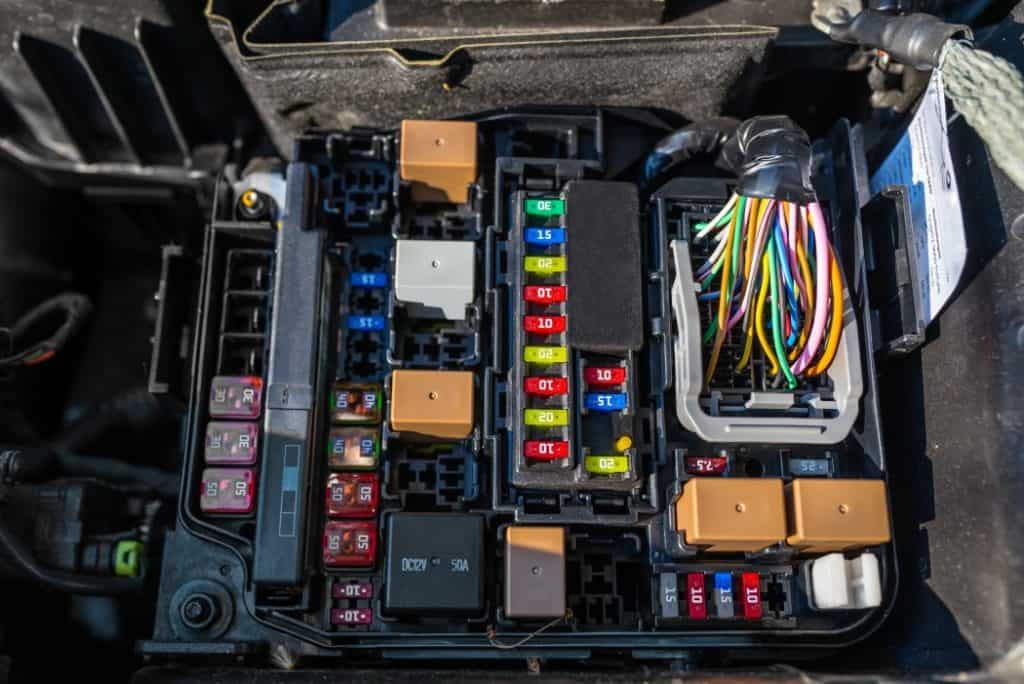

A typical fuse contains a thin conductor (usually a metal wire or strip) inside a ceramic or plastic body. When normal current flows through, the conductor remains intact. But if the current exceeds the fuse’s rated capacity—usually due to an overload or short circuit—the conductor heats up rapidly and melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the dangerous current flow.
An electric fuse essentially gives up its life to stop the flow of electricity.
Engineers design fuses to operate within very tight tolerances and publish the fuse’s characteristics in something called a time current curve. These charts show when the fuse will fail (operate) and help engineers design safe and functional circuits. When designing even a basic circuit, fuses are a critical safety feature.

When a fuse interrupts a circuit, it has protected the circuit and is considered burned or blown. Some fuses include a clear plastic window that lets you see whether the fuse is still functioning properly. If the internal conductor appears broken or discolored, the fuse has blown and requires replacement.
Other fuse types do not have a view window and require an electrical tester or a multimeter to check resistance (or continuity) across the fuse. Resistance should be near zero when operational and near infinite when blown.
⚡️ Here’s how to tell if a fuse is blown in your RV, van, or boat.
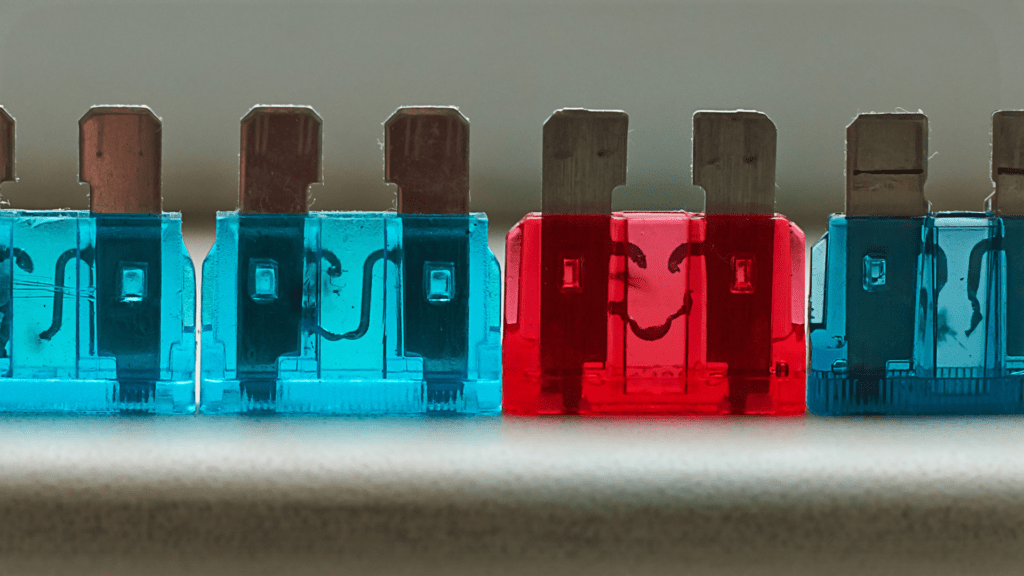
Electrical circuit protection is critically important because it identifies problems and addresses them before they cause far more severe damage.
An electrical circuit protection device can prevent electrical fires by intervening before a major fault occurs. Improper fuse protection can allow current to exceed safe levels, causing wires to overheat dangerously.
Fires can still occur when fuses are used, but it lessens the chance when a major problem occurs within the circuit.
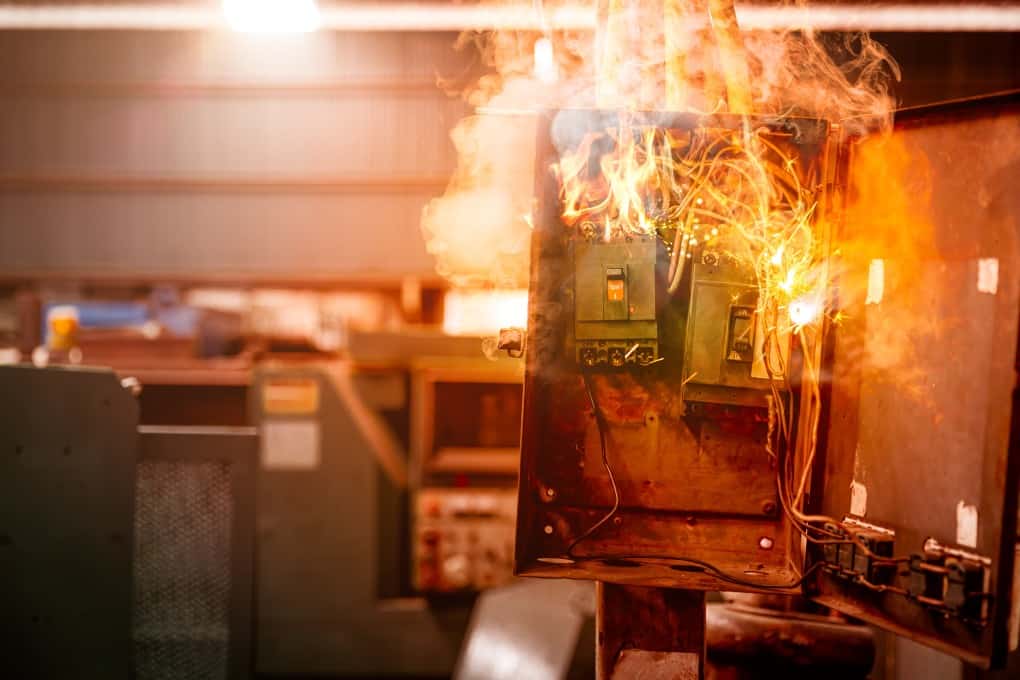

Excessive current or heat can damage or destroy expensive equipment in homes and businesses. The cost to repair or replace damaged electronics can be considerable. Proper fuse protection prevents this costly damage.
Electrical circuit protection limits fault current duration and energy, reducing the risk of sustained arcing, conductor damage, or explosive failures. Think of it kind of like a natural gas or propane supply line regulator. Major gas lines can reach 1000 PSI, which would be super dangerous in your home, so regulators are used to limit the amount of gas that can come in. Fuses are the same; when connecting to the electrical grid or batteries, enormous amounts of energy are available, but we want to make sure that the energy is a safe level for what’s using it.
In high-energy electrical faults, excessive current can jump across small gaps between conductors or damaged insulation, creating intense heat and plasma arcs. Contaminants such as dust, corrosion, or moisture can increase this risk. Limiting fault energy with proper fusing helps prevent these dangerous conditions from escalating into fires or equipment damage.

Electrical systems use many fuse types, but most fall into a few major categories based on current rating, form factor, and application. Understanding these core types makes fuse selection much easier.
Blade fuses are common in automotive, RV, and light DC systems. They plug directly into fuse blocks and are easy to inspect and replace. Common sizes include ATO, ATC, MINI, and MICRO blade fuses, typically used for low to moderate current branch circuits.
Cylindrical fuses use a tube style body made of glass or ceramic and are found in older vehicles, appliances, and some industrial or renewable energy systems. Ceramic versions handle higher fault currents and temperatures than glass fuses.
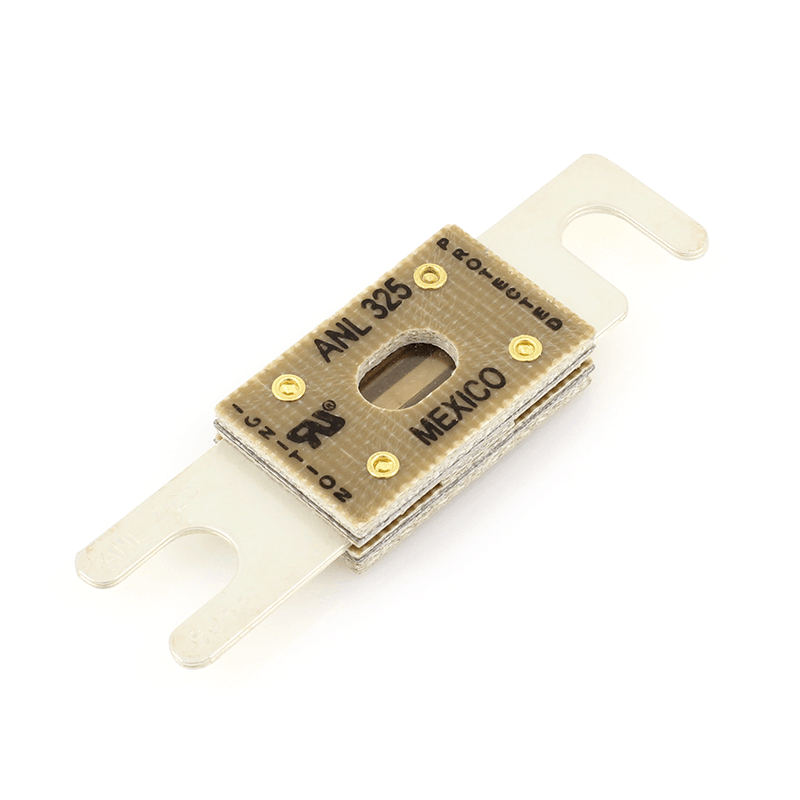
Bolt down fuses protect high-current DC circuits such as battery banks, inverters, alternators, and solar systems. These fuses mount securely with studs or bolts and include several common styles:
These fuses provide fast response and high interrupt ratings required for lithium battery systems.
Terminal fuses mount directly to a battery post and protect the main conductors feeding the system. They typically serve as the primary fuse in a DC battery system and are larger than downstream fuses.
Resettable protection devices include thermal fuses and circuit breakers that open during a fault and reset manually or automatically. While convenient, they generally respond slower than traditional fuses and are often used where reset capability is preferred over maximum fault energy limitation. Auto resetting devices need to be properly designed into a circuit however with low fault energy or can cause fires.
Some systems use specialty fuses designed for specific environments or standards, such as marine rated fuses for corrosion resistance or semiconductor fuses for sensitive electronics. These fuses address unique operating conditions rather than general circuit protection.
For Battery Systems and Solar: High-performance fuses like Battle Born MEGA Fuses are engineered for renewable energy applications. These fuses respond quickly to protect lithium battery systems from dangerous overcurrent conditions.
For Marine Applications: Marine-rated fuses withstand saltwater corrosion and harsh marine environments while providing reliable protection.
For Distribution and Protection: Fuse blocks organize multiple fuses in a single location, making system design cleaner and more professional. They’re essential for complex systems with multiple circuits.
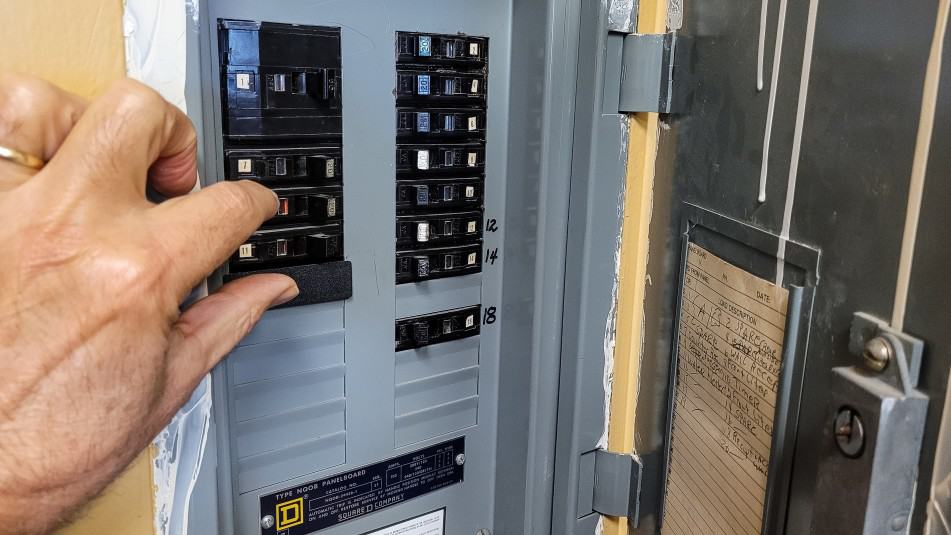

Yes, fuse quality matters.
All fuses interrupt excessive current, but higher quality fuses use tighter tolerances, higher interrupt ratings, and better internal materials. These characteristics allow the fuse to respond more predictably during fault conditions and safely interrupt high fault currents without sustained arcing, excessive heat, or internal failure.
Lower quality or improperly rated fuses may not open cleanly during a fault, may allow dangerous heat buildup, or may fail catastrophically when exposed to high fault currents. This risk increases significantly in power systems capable of delivering large amounts of current almost instantaneously. This includes large battery banks and grid-connected devices.
More expensive fuses typically reflect higher performance ratings, better construction, and certifications appropriate for demanding DC power applications. When protecting batteries, inverters, and critical wiring, fuse quality is a safety decision, not just a cost decision.
A circuit breaker acts similarly to a fuse but uses a combination of thermal (electrical heating) and magnetic components to operate a switch that opens to prevent the flow of electricity in the event of a fault. However, circuit breakers are resettable, whereas fuses need to be replaced when they operate. When a circuit breaker trips, the internal switch opens, and the electrical current stops flowing.
Circuit breakers are not a direct replacement for fuses, however. In many applications, fuses respond faster and limit fault energy more effectively than mechanical circuit breakers.
While both fuses and circuit breakers protect circuits, they work differently:
| Feature | Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Melts to break circuit | Thermal switch trips open |
| Reusability | Must be replaced after blow | Can be reset and reused |
| Response Speed | Very fast (milliseconds) | Slightly slower |
| Cost | More affordable | More expensive |
| Sensitivity | Responds quickly to overloads | Less sensitive to minor overloads |
| Best Use | Near power sources, sensitive electronics | General household circuits/places circuits regularly get overloaded |
Why choose fuses over breakers? Fuses are ideal when you need the fastest possible protection—especially near energy sources like batteries, solar panels, and power supplies. Their rapid response makes them essential for protecting sensitive electronics and preventing catastrophic failures.
Fuses are intended to be installed in circuits where they will only activate when something goes wrong. This includes near power generation/batteries and at the point of use (like electronics or motors). Circuits that can be accidentally overloaded like household 120V circuits, breakers are best.
Power Source Protection: The most critical fuse location is immediately adjacent to the power source, whether that source is a battery bank, solar array, or grid connection. Installing a fuse at the source ensures the system can interrupt a short circuit before high fault current overheats wiring or causes a fire.
At Battery Connections: In battery systems, installers typically place this primary protection directly at the battery using a terminal fuse. A terminal fuse is the largest fuse in the system and protects the main conductors feeding the rest of the electrical system. This fuse serves as the primary safeguard against catastrophic battery short circuits.
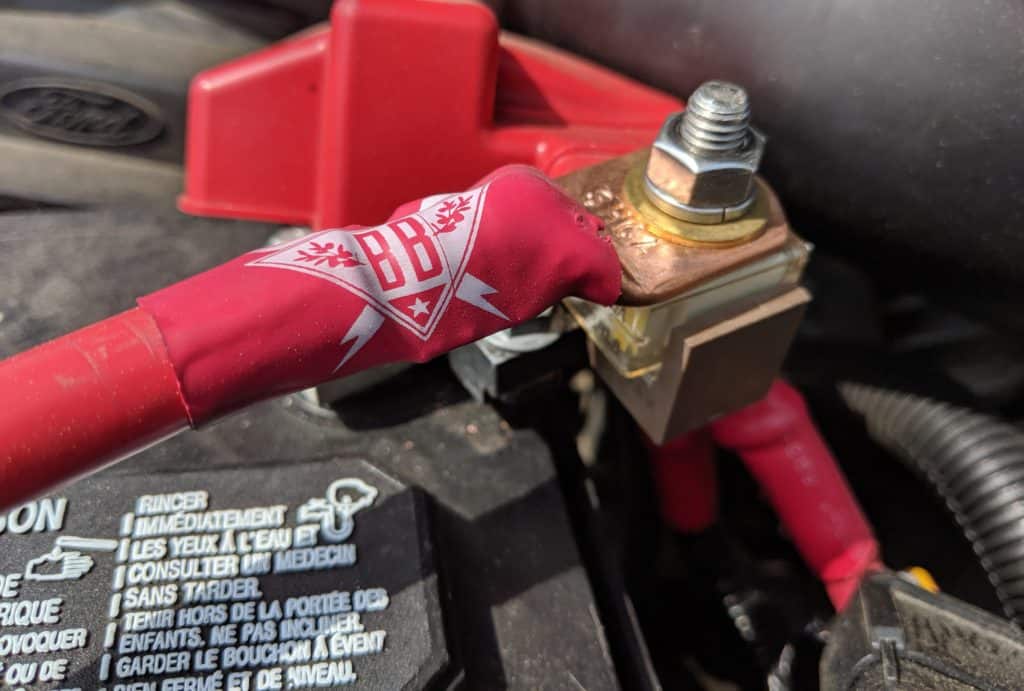

Upstream of Sensitive Loads: If the main fuse is too large for certain circuits, you may have a larger fuse at the battery and a smaller fuse on the wires coming from a distribution panel. In the event of a fault or trip, the smaller fuse will blow first, keeping the rest of the circuit online. This design method is called circuit coordination.
For example:
If a fault occurs, the smallest fuse closest to the problem blows first, keeping the rest of your system online.
For Sensitive Electronics Protection: Designs use fuses regularly in sensitive circuitry because they react quickly and can protect sensitive electronic devices such as navigation systems, audio equipment, battery management systems, and solar charge controllers. Fuses are even used in the electric grid for this reason.
In Complex Systems: Fuses play a critical role in safe battery systems, including off-grid solar, RV power systems, marine systems, and renewable energy installations. Browse our complete fuse options to find the right solution for your application.
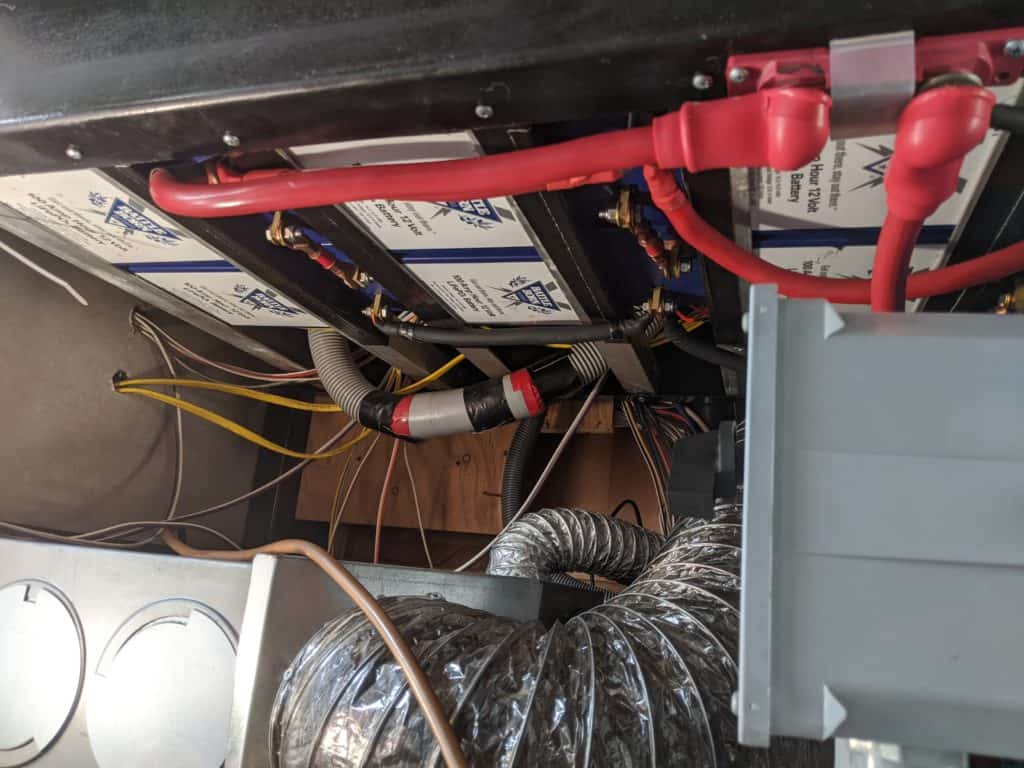

Selecting the correct fuse size is critical; undersized fuses cause frustrating nuisance trips, while oversized fuses defeat the purpose of protection.
To choose the appropriate size electrical fuse for a given application, we need to calculate the maximum current that the circuit we’re powering will draw continuously. (The maximum amperage that the device we’re powering will draw under sustained load.)
Next, we need to select an electric fuse that is 125% larger than the maximum current expected to flow through the circuit. This 125% factor applies to continuous current, not short-duration surge or startup currents.
In this case, you would select the next standard fuse size at or above the calculated value, commonly 350A or 400A, depending on available fuse sizes and the ampacity of the installed wiring.
Finally, verify your wire sizing. The fuse rating must not exceed the current-carrying capacity of the wire being protected. If smaller gauge wires are used, a smaller fuse must be selected to protect them.
In many DC power systems, designers select fuses to protect the wire rather than just the connected equipment. In these cases, the fuse rating must not exceed the wire’s safe current-carrying capacity, or ampacity.
For DC applications common in RV, marine, and off-grid renewable energy systems, the following fuse sizes are typical maximums when using copper conductors with high-temperature insulation (90 °C), installed in free air:
Actual allowable fuse size depends on insulation type, ambient temperature, cable routing, and applicable electrical standards. When in doubt, consult manufacturer’s ampacity charts or system documentation.
Using an oversized fuse can allow wiring to overheat before protection activates, increasing the risk of equipment damage or fire.
The right fuses depend on your application:
In RV, marine, and off grid battery systems, proper fuse selection is one of the most important and most commonly overlooked safety considerations.
A correctly fused circuit will not overheat in the event of an overload because the fuse will blow. The fuse exists as a protective mechanism to stop the flow of current so that a fault will not have the opportunity to create excessive heat or an explosion.
Because this outcome is never what you want in an electrical system, fuses very much matter in your system installation! Because of this, it is important not to skimp on this critical piece of equipment. Read on to learn Why You Should Invest In Fuses For Your System.
Ready to protect your electrical system? Browse our complete fuse selection and find the right solution for your application.
Q: What is the function of a fuse?
A: A fuse protects electrical wiring and equipment by interrupting the flow of electricity when current exceeds safe levels. It acts as a deliberate weak link in the circuit, melting or opening during a fault to prevent overheating, fire, or equipment damage.
Q: What is the difference between a breaker and a fuse?
A: Both protect electrical circuits, but they operate differently. A fuse permanently opens a circuit when excessive current melts its internal element, requiring replacement after it operates. A circuit breaker opens a mechanical switch using thermal and magnetic sensors during a fault and allows you to reset the circuit once the issue is resolved. Fuses typically respond faster and limit fault energy more effectively, which makes them a common choice near batteries and sensitive electronics.
Q: What happens if I install a fuse that’s too large?
A: An oversized fuse may not operate when a fault occurs, allowing excessive current to flow. This can cause wires to overheat, damage equipment, or create a serious fire risk. A fuse that’s too large defeats the purpose of circuit protection.
Q: What happens if I install a fuse that’s too small?
A: An undersized fuse will blow during normal operation, causing nuisance trips and system interruptions. This often happens when designers fail to account for continuous current or startup current during fuse selection.
Q: How do I know if a fuse has blown?
A: Some fuses include a visual indicator or inspection window showing a broken conductor. Others require testing with a multimeter or continuity tester. If a circuit suddenly stops working, a blown fuse is often the first thing to check.
Q: Do lithium battery systems require different fuses than lead-acid systems?
A: The fuse sizing method is the same, but lithium batteries can deliver higher and more sustained currents than lead-acid batteries. Because of this, lithium systems often require higher-quality fuses with appropriate interrupt ratings to safely handle potential fault currents.
Q: What is a MEGA fuse?
A: A MEGA fuse is a small but high-current fuse commonly used in battery systems, inverters, and renewable energy installations. MEGA fuses are designed to safely interrupt large DC fault currents while minimizing sustained arcing, making them ideal for high-power lithium battery systems.
Q: Can a fuse prevent damage from a short circuit?
A: Yes. A properly sized fuse limits the duration and energy of a short circuit, reducing the risk of sustained arcing, wire damage, fire, and catastrophic equipment failure. While no protection device can eliminate all risk, fuses are a critical safety component.
Q: How often should fuses be replaced?
A: Fuses do not wear out under normal operation and only need to be replaced after they operate. If a fuse blows repeatedly, it’s a sign of an underlying electrical issue that should be diagnosed before installing a replacement.
Q: Is it okay to temporarily bypass a fuse?
A: No. Bypassing a fuse removes critical circuit protection and can lead to severe equipment damage, fire, or personal injury. If a fuse continues to fail, the root cause should be identified and corrected rather than bypassing the protection.
We know that building or upgrading an electrical system can be overwhelming, so we’re here to help. Our Reno, Nevada-based sales and customer service team is standing by at (855) 292-2831 to take your questions!
Also, join us on Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube to learn more about how lithium battery systems can power your lifestyle, see how others have built their systems, and gain the confidence to get out there and stay out there.
Shop Best Sellers








Ask a technical specialist now at 855.292.2831
Stay in the Know
One thought on “What Is An Electric Fuse and Why Do They Matter?”
You didn’t mention the fuses that light up when they blow. I changed out most of mine to those.